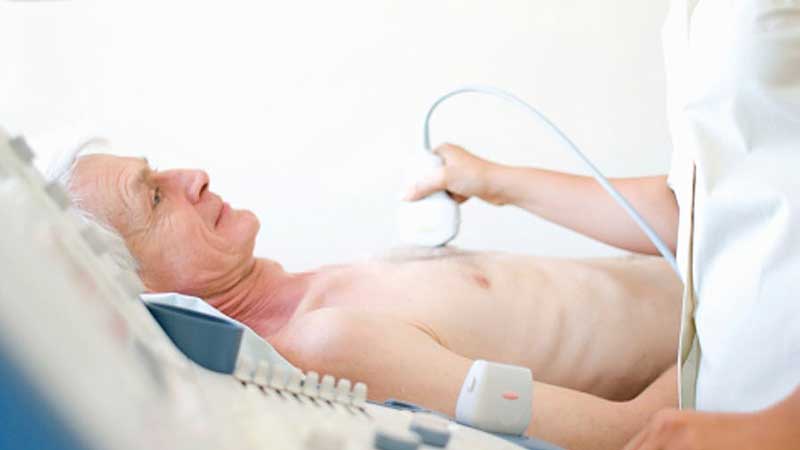
An echo test, commonly known as an echocardiogram, is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to assess the heart’s function and structure. This test uses sound waves to create images of the heart, helping doctors evaluate the condition of the heart valves, chambers, and overall blood flow. If you’re wondering why an echo test is done, it’s typically used when there are concerns about heart diseases, such as heart failure, valve issues, or congenital heart conditions. It offers a clear view of how well the heart is pumping blood and whether there are any abnormalities. This test is essential for diagnosing various heart-related conditions and monitoring existing cardiac issues to prevent further complications.
What is an Echo Test?
An echo test uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the heart. This imaging technique is commonly performed in a hospital or outpatient setting, with the patient typically lying on an exam table. The procedure is painless and involves applying a gel to the chest area, followed by placing a small device called a transducer that emits sound waves. The sound waves bounce off the heart structures, and the resulting images are captured to provide an inside view of the heart’s condition. Echo tests are essential for diagnosing various heart conditions, from valve abnormalities to blood flow problems.
Why is an Echo Test Done?
Echo tests are performed to assess the heart’s function and detect any potential problems. One of the primary reasons for conducting an echo test is to investigate symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue. This test can help identify issues like heart valve malfunctions, heart failure, and congenital defects that may be contributing to these symptoms. Echo tests are also crucial for monitoring patients with existing heart conditions to track any changes over time. Early detection through echo tests can prevent serious complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Types of Echo Tests
There are several types of echocardiograms, each serving a unique purpose in diagnosing specific heart conditions. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is the most common type, where the transducer is placed on the chest. For a more detailed examination, a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is used, where the transducer is passed down the throat to get a closer look at the heart. Stress echocardiograms involve monitoring the heart during physical activity, usually on a treadmill or stationary bike, to evaluate heart function under stress. These various types of echo tests provide invaluable insight into the heart’s health from different perspectives.
Conditions Diagnosed by Echo Test
An echo test is a valuable diagnostic tool for a range of heart-related conditions. It can help diagnose heart valve problems, such as valve stenosis or regurgitation, where the valves don’t function properly. The test also aids in detecting heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. Echo tests are also used to identify congenital heart defects, such as holes in the heart or abnormal heart chambers. By providing a clear image of the heart’s structure, echo tests allow doctors to determine the severity of these conditions and recommend the best treatment options.
How the Echo Test Helps in Heart Failure Diagnosis
For individuals suspected of having heart failure, an echo test is an essential diagnostic tool. The test helps doctors evaluate how well the heart is pumping blood and whether any heart chambers are enlarged or weakened. By assessing the heart’s ejection fraction, the echo test can help determine how much blood the heart pumps out with each beat. A lower ejection fraction may indicate heart failure, a condition that can progressively worsen without appropriate treatment. An early diagnosis through an echo test can allow doctors to implement timely interventions to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Vote
Who is your all-time favorite president?
Monitoring Heart Conditions with Echo Tests
For individuals with existing heart conditions, regular echo tests are often necessary to monitor any changes in heart function. Conditions such as valve diseases, heart failure, or arrhythmias require ongoing evaluation to track the effectiveness of treatments and interventions. Echo tests can detect any changes in the heart’s structure or function, providing doctors with essential information to adjust treatment plans. Patients with pacemakers or artificial heart valves may also undergo echo tests periodically to ensure the devices are functioning correctly. Consistent monitoring allows for early intervention and better long-term management of heart-related issues.
Preparing for an Echo Test
Preparing for an echo test is simple and non-invasive. There are generally no special preparations required, although your doctor may ask you to refrain from eating or drinking for a few hours before the test, especially for a transesophageal echo. During the test, you will lie on your back or side while the technician applies the gel to your chest. It’s important to remain as still as possible during the test to ensure the images are clear and accurate. You may also be asked to hold your breath briefly at times to help obtain better pictures of your heart.
What to Expect During the Echo Test
During the echo test, a technician will use a handheld device called a transducer to send sound waves into your body. These sound waves bounce back from your heart, and the device records the results to create images. The procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes to an hour and is entirely painless. Most people are able to resume their normal activities immediately after the test. Depending on the type of echo test, such as a stress echo, you may also be asked to perform some physical activity to monitor how your heart responds under stress.
Risks and Side Effects of Echo Tests
Echo tests are considered safe with minimal risk. Since they do not involve radiation or invasive procedures, they are far less risky than other imaging methods such as X-rays or CT scans. The most common side effects may include temporary skin irritation from the gel or slight discomfort from the pressure of the transducer. In rare cases, a transesophageal echo may cause throat irritation or gagging. However, serious complications from echo tests are extremely rare, and they are considered one of the safest diagnostic tools for heart health.
Benefits of Echo Tests
Echo tests offer numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers. These tests provide real-time, detailed images of the heart, helping doctors diagnose conditions accurately and monitor treatment effectiveness. Echo tests are non-invasive, meaning there is no need for surgery or incisions. They are also painless and can be performed quickly, offering fast results that aid in making timely decisions about treatment. Additionally, echo tests are widely available, cost-effective, and can be performed without the need for hospitalization, making them a convenient option for many patients.
Reasons to Get an Echo Test
- To diagnose heart conditions like heart failure or valve disease
- To monitor existing heart conditions
- To evaluate unexplained symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath
- To check for congenital heart defects
- To assess heart function before surgery
- To guide treatment decisions, such as medication or surgery
- To track the effectiveness of heart disease treatments
Watch Live Sports Now!
Dont miss a single moment of your favorite sports. Tune in to live matches, exclusive coverage, and expert analysis.
Start watching top-tier sports action now!
Watch NowSteps in the Echo Test Procedure
- Application of gel to the chest
- Placement of the transducer on the chest or in the throat
- Capture of sound waves reflected by the heart
- Image processing to create heart visuals
- Review of the images by the technician
- Analysis of results by the cardiologist
- Discussion of findings and next steps
Pro Tip: If you have any concerns about the echo test, speak with your healthcare provider beforehand to understand the procedure and set realistic expectations. It can also help to bring a list of any current medications or existing heart issues to the appointment for more accurate results.
| Test Type | Purpose | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Transthoracic Echo | Non-invasive heart imaging | 30-60 minutes |
| Transesophageal Echo | Detailed view of heart structures | 60-90 minutes |
| Stress Echo | Evaluate heart function under stress | 30-45 minutes |
“An echo test provides an in-depth view of your heart, helping you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your heart health.”
If you’re experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, breathlessness, or fatigue, an echo test may be the key to understanding what’s happening inside your heart. Don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor about whether this diagnostic tool is right for you. Regular heart health assessments can make all the difference in preventing more severe issues down the line. Bookmark this page for future reference and share it with friends and family who may benefit from learning about echo tests. Remember, heart health matters, and early detection through echo tests is one of the best ways to ensure a long and healthy life.