Harnessing Profitability through Regenerative Agriculture!
Introduction:
Regenerative agriculture is more than just a farming technique; it’s a holistic approach aimed at restoring and enhancing ecosystem functions while increasing farm profitability. By focusing on soil health, biodiversity, and ecological balance, regenerative agriculture offers numerous benefits to farmers while mitigating environmental degradation. In this article, we will explore how regenerative agriculture practices can lead to profitable farming.
-
Soil Health and Fertility:
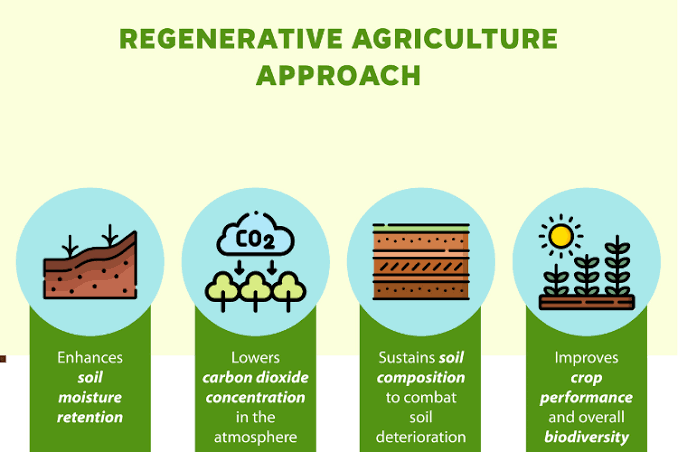
Regenerative agriculture prioritizes soil health as the foundation of farming success. By adopting practices such as minimal tillage, cover cropping, and crop rotation, farmers can enhance soil structure, organic matter content, and microbial activity. Healthy soils promote better nutrient uptake by plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. As a result, farmers can save on input costs while achieving higher yields and improved crop quality. -
Carbon Sequestration:
One of the key principles of regenerative agriculture is carbon sequestration, which involves capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide and storing it in the soil. Practices like agroforestry, rotational grazing, and no-till farming enhance carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change while improving soil fertility. Farmers can also participate in carbon markets or receive incentives for implementing carbon-friendly practices, providing an additional source of income. -
Water Management:
Efficient water management is crucial for agricultural sustainability, especially in regions prone to drought or water scarcity. Regenerative agriculture practices such as contour farming, mulching, and the use of cover crops help improve water retention in the soil, reducing the need for irrigation and preventing soil erosion. By conserving water resources, farmers can lower their operating costs and increase resilience to climate variability. -
Biodiversity Enhancement:
Regenerative agriculture encourages the preservation and enhancement of biodiversity on farmland. By creating diverse habitat corridors, planting hedgerows, and incorporating native plants, farmers can attract beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife that contribute to pest control and pollination. Increased biodiversity also leads to more resilient ecosystems, reducing the risk of crop failure and the need for chemical inputs. -
Economic Viability:
While some may perceive regenerative agriculture as costly or labor-intensive, it offers significant long-term economic benefits for farmers. By reducing reliance on external inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, farmers can lower production costs and improve profit margins. Moreover, regenerative practices often result in higher-quality crops, which can command premium prices in the market. Additionally, adopting regenerative agriculture can enhance the value of farmland over time, making it a sound investment for future generations. -
Resilience to Climate Change:
In an era of increasing climate uncertainty, regenerative agriculture provides a pathway for farmers to build resilience and adaptability. By improving soil health, diversifying crop rotations, and implementing agroecological practices, farmers can mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves. This resilience not only protects farm productivity but also ensures food security for communities and nations. -
Consumer Demand and Market Opportunities:
There is a growing demand for sustainably produced food and agricultural products among consumers worldwide. By adopting regenerative agriculture practices, farmers can tap into this market demand and differentiate their products based on environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Moreover, certifications such as USDA Organic, Regenerative Organic Certified, and Fair Trade provide farmers with access to premium markets and higher price premiums, further enhancing profitability.
Conclusion:
Regenerative agriculture offers a pathway to profitable farming by prioritizing soil health, carbon sequestration, water management, biodiversity enhancement, economic viability, resilience to climate change, and market opportunities. By embracing regenerative practices, farmers can improve their bottom line while contributing to environmental conservation and sustainable development. As we look towards the future of agriculture, regenerative principles will play a central role in shaping a more resilient, equitable, and prosperous food system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VEZvF68sytc