Leukemia, a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, can have a profound impact on a person’s health. It is caused by an abnormal growth of white blood cells, leading to problems with normal blood cell production. While some cases of leukemia are hereditary, others arise due to environmental factors or unknown causes. Understanding the genetic factors and available treatments for leukemia is crucial for those affected by the disease and their families. Let’s explore the genetic causes, types of leukemia, and treatments in detail, to provide a clearer picture of what people with leukemia face and how advancements in medical science are helping improve their prognosis.
What is Leukemia?
Leukemia is a type of cancer that begins in the bone marrow, affecting the body’s ability to produce normal blood cells. It primarily affects white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infection. Leukemia leads to the production of abnormal, immature white blood cells that don’t function properly. As these abnormal cells multiply, they crowd out healthy cells, causing a range of symptoms. Early detection is vital, as it can help initiate treatments before the disease progresses further.
Genetic Causes of Leukemia
Genetic mutations are a significant cause of leukemia. Chromosomal abnormalities are often seen in leukemia patients, such as the Philadelphia chromosome, which is a fusion of two genes (BCR-ABL). These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, making leukemia cells multiply rapidly. Other inherited genetic conditions, like Down syndrome or Fanconi anemia, can also increase the risk of developing leukemia. Although genetics plays a role, environmental factors such as exposure to radiation or chemicals may also contribute to the disease.
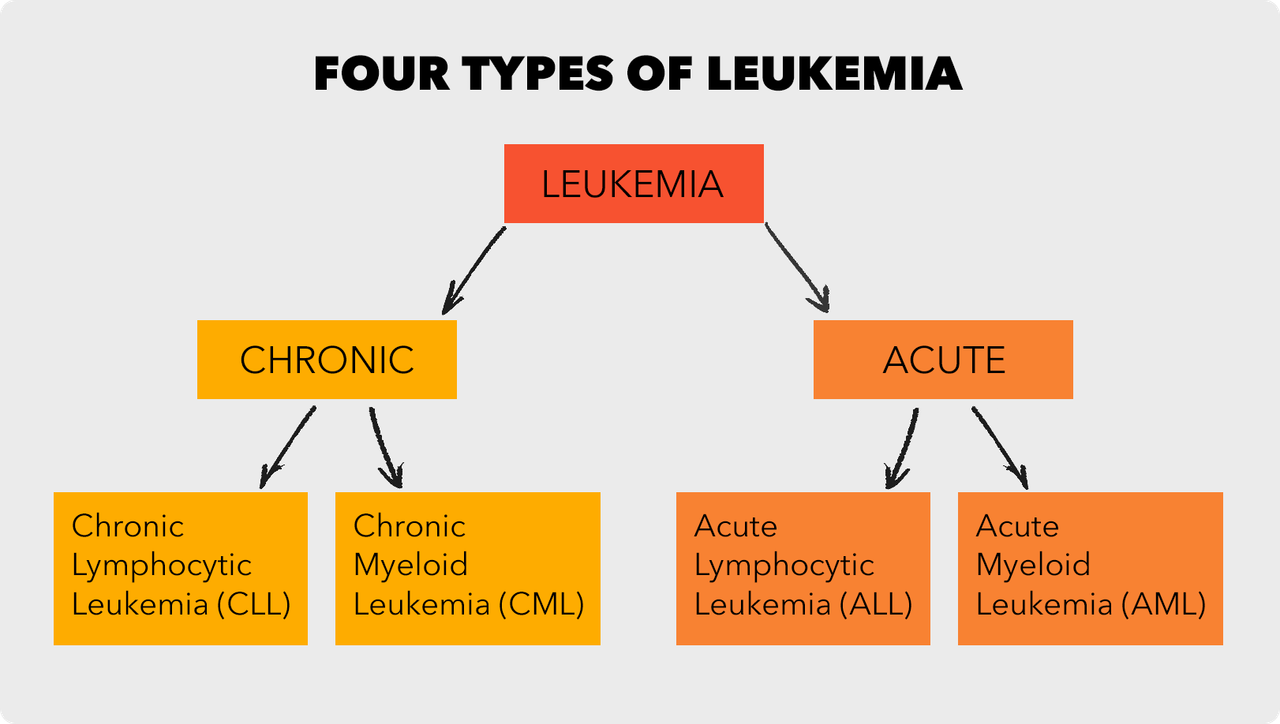
Types of Leukemia
Leukemia is categorized into several types based on the kind of blood cell affected and how quickly the disease progresses. The two main types of leukemia are acute and chronic, with the former developing rapidly and the latter progressing more slowly. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are examples of lymphoid leukemias, while acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) are types of myeloid leukemia. Each type has different causes, symptoms, and treatments, making it essential for doctors to correctly diagnose the specific form. Proper classification is key to determining the most effective treatment plan.
Risk Factors for Leukemia
In addition to genetic mutations, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing leukemia. Family history plays a role, as individuals with close relatives who had leukemia may have a higher chance of developing it themselves. Other factors include exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene, or prior treatments for other cancers that involved chemotherapy or radiation. People with certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome or neurofibromatosis, are also at an elevated risk. Age is another factor, as leukemia is more common in older adults and young children.
Symptoms of Leukemia
Symptoms of leukemia can vary depending on the type of leukemia and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms include fever, unexplained weight loss, frequent infections, and easy bruising or bleeding. Fatigue, pale skin, and swollen lymph nodes are also common signs of leukemia. As leukemia progresses, it can cause pain in the bones or joints and a general feeling of illness. Early diagnosis is essential to start treatment before the disease leads to more severe complications.
Vote
Who is your all-time favorite president?
Diagnosis of Leukemia
Leukemia is diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, and bone marrow biopsies. Blood tests can reveal an abnormal increase in white blood cells, which is often the first sign of leukemia. A bone marrow biopsy is then performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of leukemia. Doctors may also use imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, to check for enlarged lymph nodes or other abnormalities. Genetic testing is essential for identifying specific mutations, which helps guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Leukemia
Treatment for leukemia depends on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient’s overall health. The primary treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted therapies. Chemotherapy is the most common treatment and involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells. Stem cell transplants can help restore healthy bone marrow, while targeted therapies specifically target leukemia cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. Immunotherapy, which uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, is also being explored as an alternative treatment.
Advances in Leukemia Treatment
Recent advances in leukemia treatment have significantly improved survival rates. One such advancement is the development of targeted therapies, which focus on specific genetic mutations that drive leukemia. Immunotherapy has also shown promise, as it can help the body’s immune system attack leukemia cells more effectively. CAR-T cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy, has been used to treat certain types of leukemia with positive results. These innovative treatments offer hope for better outcomes, particularly for those who do not respond well to traditional therapies.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for leukemia patients depends on various factors, such as the type of leukemia, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s age and overall health. Survival rates have increased in recent decades due to improvements in early detection and treatment options. For example, the five-year survival rate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is around 90% in children, while it can be lower in adults. Chronic types of leukemia, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), tend to have a better long-term prognosis. However, survival rates can vary widely based on individual circumstances.
Supporting Leukemia Patients
Supporting individuals with leukemia involves more than just medical treatment. Emotional and psychological support plays an important role in helping patients cope with the challenges of the disease. Families, friends, and support groups can offer invaluable assistance during treatment. Nutrition, physical therapy, and palliative care are also crucial in improving the quality of life for leukemia patients. Providing ongoing emotional support and care can make a significant difference in a patient’s recovery and overall well-being.
Risk Factors for Leukemia
- Family history of leukemia
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene
- Previous chemotherapy or radiation treatment
- Genetic conditions such as Down syndrome
- Age, with higher rates in young children and older adults
- Viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus
- Exposure to high levels of radiation
Watch Live Sports Now!
Dont miss a single moment of your favorite sports. Tune in to live matches, exclusive coverage, and expert analysis.
Start watching top-tier sports action now!
Watch NowTreatment Options for Leukemia
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Stem cell transplants
- Targeted therapies
- Immunotherapy
- Bone marrow biopsy for diagnosis
- Clinical trials for new treatments
Pro Tip: Early detection and genetic testing play a crucial role in choosing the right treatment options for leukemia patients.
| Aspect | Positive Outcome | Negative Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Testing | Helps determine the best course of treatment | Can be costly and may not be available in all areas |
| Chemotherapy | Effective in killing leukemia cells | May cause severe side effects, including nausea and hair loss |
| Immunotherapy | Can significantly improve survival rates for some patients | Still being studied for its long-term effectiveness |
“The fight against leukemia is not just a battle for survival, but a testament to the strength of the human spirit.”
Leukemia remains a challenging disease, but with advancements in genetic understanding and treatment options, more people are surviving and thriving after diagnosis. If you or someone you know is affected by leukemia, it’s important to seek medical advice early and explore all treatment options available. Share this blog to raise awareness about leukemia’s genetic causes and treatments, and consider supporting leukemia research or local support groups. Bookmark this article as a resource for more information, and keep the conversation going on social media. Together, we can continue to push forward in the fight against leukemia.