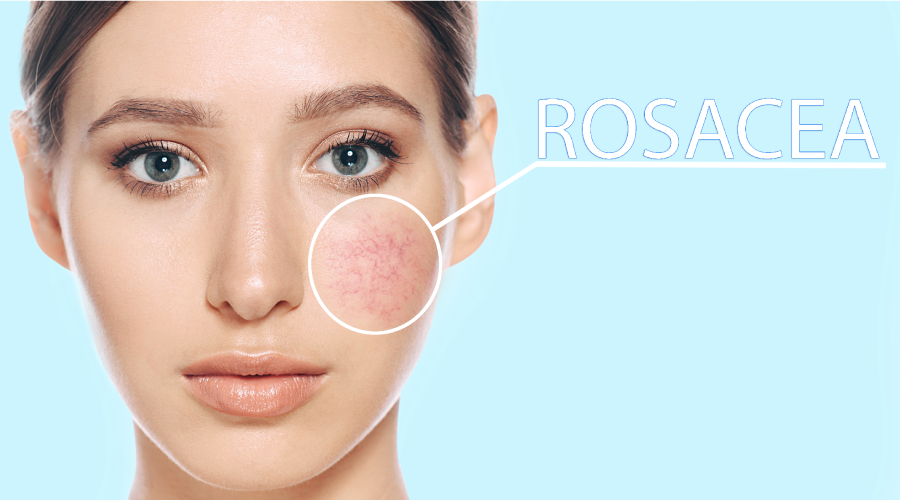
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes redness, visible blood vessels, and even pimples, typically on the face. While there is no known cure for rosacea, there are several ways to manage its symptoms effectively. With the right treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and skincare routines, rosacea can be controlled, and flare-ups can be minimized. In this guide, we’ll explore the most effective methods to get rid of rosacea permanently, helping you regain clear and smooth skin.
Understanding Rosacea
Before diving into treatments, it’s important to understand what causes rosacea. This skin condition typically affects fair-skinned individuals and is more common in women, especially those over 30. While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers play a role. Common symptoms include persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and pimple-like bumps on the cheeks, nose, and forehead. Identifying triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, or extreme weather can help manage flare-ups and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Topical Treatments for Rosacea
One of the most common treatments for rosacea is the use of topical medications. These creams and gels help reduce inflammation and redness. Medications like metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin are often prescribed by dermatologists to control rosacea symptoms. These treatments work by decreasing inflammation and reducing the number of visible blood vessels. Consistent application, as directed by a healthcare provider, can significantly improve the appearance of the skin over time.
Oral Medications for Rosacea
In cases where topical treatments are not enough, oral medications may be prescribed to manage rosacea symptoms. Antibiotics such as tetracycline or doxycycline are often used to reduce inflammation and control breakouts. Oral medications can be particularly helpful for individuals with severe rosacea or those experiencing widespread redness. Additionally, low-dose oral isotretinoin may be considered for individuals with persistent symptoms. It’s crucial to work with your doctor to determine the appropriate oral treatment based on the severity of your rosacea.
Laser and Light Therapy
Laser treatments have become an increasingly popular option for those with rosacea, especially for reducing visible blood vessels. Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy and laser resurfacing are commonly used to treat the redness and broken capillaries associated with rosacea. These treatments work by targeting the blood vessels beneath the skin’s surface, helping to minimize redness and improve skin texture. While results vary, many patients experience long-lasting improvement after a series of treatments. Consulting with a dermatologist experienced in laser therapy is essential to achieving the best results.
Skincare Routine for Rosacea
Establishing a gentle skincare routine is crucial for managing rosacea. Using mild, fragrance-free products that are formulated for sensitive skin can help reduce irritation. Avoiding harsh scrubs and alcohol-based toners is essential, as they can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Incorporating a soothing moisturizer that helps maintain the skin’s moisture barrier is also important. Regularly applying sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 can protect the skin from sunburn, a common rosacea trigger.
Vote
Who is your all-time favorite president?
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Diet and lifestyle changes can play a significant role in controlling rosacea. Avoiding known triggers such as hot drinks, spicy foods, and alcohol can help prevent flare-ups. Some studies suggest that anti-inflammatory foods like green tea, omega-3-rich fish, and leafy greens may help reduce rosacea symptoms. Staying hydrated and managing stress through relaxation techniques can also help prevent flare-ups. Keeping a food and lifestyle diary can help identify your specific triggers and adjust your habits accordingly.
Stress Management for Rosacea
Stress is one of the most common triggers for rosacea flare-ups. Reducing stress through mindfulness practices, yoga, or regular exercise can help keep symptoms under control. Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation can significantly lower stress and improve skin health. Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation in the body, which in turn, may worsen rosacea symptoms. Prioritizing stress management is an important step toward achieving long-term rosacea relief.
Using Natural Remedies
Natural remedies are often sought by those looking to complement their medical treatment for rosacea. Ingredients like aloe vera, chamomile, and green tea have anti-inflammatory properties that may help soothe the skin. Applying a cold compress to the face or using natural oils such as rosehip oil may also help reduce redness and irritation. However, it’s important to patch-test any natural remedy before applying it to the face to ensure it doesn’t cause further irritation. While natural remedies can offer temporary relief, they should be used in conjunction with medical treatments for long-term rosacea management.
The Importance of Sun Protection
Exposure to sunlight is one of the most common rosacea triggers. Protecting your skin from the sun is vital for preventing flare-ups and managing symptoms. Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day can shield your skin from harmful UV rays. Wearing a wide-brimmed hat and avoiding peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) can provide additional protection. Sun protection should be an integral part of your daily skincare routine, especially for those prone to rosacea flare-ups.
When to See a Dermatologist
While rosacea can often be managed with lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter treatments, it’s important to see a dermatologist if symptoms worsen or persist. A dermatologist can offer prescription treatments, such as topical or oral medications, and recommend advanced therapies like laser treatment. In severe cases, a dermatologist may also help rule out other skin conditions that could mimic rosacea symptoms. Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring progress and adjusting treatments as necessary. A personalized approach to managing rosacea will help you achieve the best possible results.
Key Steps to Manage Rosacea
- Avoid triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and hot drinks.
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products that are suitable for sensitive skin.
- Apply sunscreen daily to protect from UV rays.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
- Incorporate stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine.
- Consult a dermatologist for personalized treatment options.
- Consider laser or light therapy for visible blood vessels.
Watch Live Sports Now!
Dont miss a single moment of your favorite sports. Tune in to live matches, exclusive coverage, and expert analysis.
Start watching top-tier sports action now!
Watch NowEffective Treatments for Rosacea
- Topical medications like metronidazole or azelaic acid.
- Oral antibiotics for severe cases of rosacea.
- Laser treatments to reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
- Consistent use of sunscreen to prevent sun-induced flare-ups.
- Natural remedies like aloe vera and green tea for temporary relief.
- Stress management through yoga or mindfulness practices.
- Regular skincare routine with gentle, hydrating products.
Pro Tip: Keeping track of your rosacea triggers through a daily journal can help you identify what causes flare-ups and tailor your skincare and lifestyle choices to manage symptoms effectively.
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Medications | Moderate | Ongoing |
| Laser Treatments | High | 3-6 months |
| Diet and Lifestyle Changes | Moderate | Ongoing |
“Managing rosacea requires a combination of treatment, lifestyle changes, and careful attention to triggers. With the right approach, you can take control of your skin health.”
By following a consistent routine and working closely with a healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your rosacea and enjoy clear, healthy skin. Take action today to identify triggers and begin treatments that work for you. If you’re ready to see real results, consult with a dermatologist and explore personalized treatment options. Don’t let rosacea control your life—take charge of your skin health and enjoy the confidence that comes with it. Share this post with others who may benefit from these tips and don’t forget to bookmark it for future reference!