Dopamine, often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, plays a crucial role in shaping our social interactions. It’s the brain chemical that drives motivation, pleasure, and reward, and its influence extends far beyond just how we experience happiness. Our interactions with others trigger dopamine release, reinforcing social bonds and encouraging us to seek more positive connections. Understanding dopamine’s role in social behavior can provide valuable insights into how we form relationships, build trust, and experience emotional rewards. This article will explore how dopamine influences social interactions, from the way we bond with friends and family to its impact on our broader social experiences.
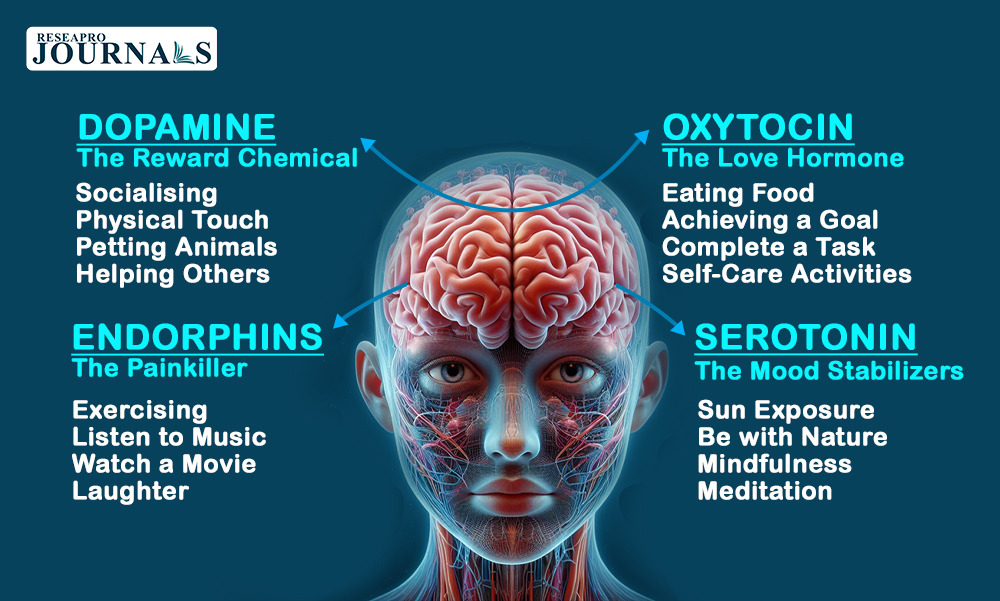
What is Dopamine and How Does It Work?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays an essential role in the brain’s reward system. It helps regulate emotional responses, motivation, and pleasure, and is released when we achieve something rewarding, such as completing a task or receiving recognition. When dopamine is released during positive social interactions, it reinforces behaviors that lead to more social engagement. This reinforces our desire to interact with others and can contribute to feelings of satisfaction and connection. Dopamine’s role in reward is critical to understanding human social behavior and motivation.
Dopamine and Social Bonding
Dopamine is directly linked to the formation of social bonds. Positive social experiences, like laughing with friends or receiving compliments, trigger the release of dopamine in the brain. These rewarding experiences create emotional memories that strengthen the desire to engage with others, leading to closer relationships. Mutual dopamine release during social interactions strengthens emotional connections and fosters a sense of belonging. When dopamine levels are high, people tend to feel more connected and motivated to nurture their relationships.
The Dopamine Response to Social Recognition
One of the primary ways dopamine influences social interaction is through the feeling of social recognition. Whether it’s a compliment, praise at work, or a simple act of kindness, social acknowledgment triggers dopamine release, enhancing feelings of self-worth. This positive reinforcement encourages individuals to seek out similar interactions to replicate the rewarding feeling. Social recognition boosts dopamine levels, making people feel valued and appreciated. Consequently, it drives them to engage in more positive social behaviors and interactions.
How Dopamine Affects Communication
Effective communication relies heavily on social feedback, which in turn triggers dopamine release. When we engage in a conversation and receive validation or positive responses, dopamine is released, reinforcing the behavior. Good communication fosters stronger social connections and encourages continued interaction. This feedback loop keeps us motivated to participate in social exchanges, from casual conversations to more in-depth discussions. Dopamine enhances communication skills by rewarding successful interactions.
The Impact of Dopamine on Empathy
Empathy, or the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, is also influenced by dopamine. When we empathize with someone, especially during a meaningful conversation, our brain releases dopamine in response to their emotions. This release strengthens our emotional connection with others and motivates us to continue supporting them. Empathy enhances social bonds and encourages prosocial behaviors, reinforcing the importance of emotional connections. Dopamine, therefore, plays a key role in fostering deep, meaningful relationships.
Vote
Who is your all-time favorite president?
Dopamine and Social Anxiety
While dopamine is generally associated with positive social interactions, an imbalance in dopamine levels can contribute to social anxiety. Low dopamine levels may reduce motivation and lead to feelings of fear and discomfort in social settings. On the other hand, an excess of dopamine may result in overstimulation, leading to restlessness and difficulty focusing during social interactions. Finding balance in dopamine production is essential for managing social anxiety and ensuring positive social experiences. A stable dopamine level can encourage individuals to engage more comfortably in social environments.
Dopamine and Group Dynamics
In group settings, dopamine helps to enhance social cohesion by encouraging cooperation and shared experiences. Group activities, whether they are professional collaborations or casual gatherings, trigger dopamine release when everyone participates in a positive way. Shared experiences foster trust and mutual respect, which in turn strengthens group dynamics. Dopamine’s role in enhancing group cohesion is important in both personal and professional settings. By encouraging positive social exchanges, dopamine plays a part in creating strong, effective teams.
The Role of Dopamine in Romantic Relationships
Dopamine is essential for creating and maintaining romantic relationships. Early stages of romantic relationships are often marked by a rush of dopamine, which creates feelings of excitement, attraction, and pleasure. As the relationship develops, dopamine continues to reinforce emotional bonding, encouraging partners to stay connected and engaged. Romantic interactions trigger dopamine, which helps maintain intimacy and affection between partners. This neurotransmitter strengthens the emotional foundation of the relationship, making it more fulfilling.
Dopamine and Social Media Interaction
In today’s digital age, social media has become a significant driver of dopamine release. Every like, comment, or notification can stimulate dopamine, encouraging individuals to engage more frequently with online platforms. Social media creates a constant dopamine loop, reinforcing the desire for validation and social connection. This can be both positive and negative, as it can lead to dependency on external validation for emotional satisfaction. While social media fosters connection, it is important to balance online and offline interactions to avoid dopamine overload.
Managing Dopamine Levels for Healthy Social Interactions
Maintaining a healthy balance of dopamine is crucial for optimal social interactions. Too little dopamine can result in apathy and withdrawal from social settings, while too much can lead to overstimulation and anxiety. Healthy habits, such as regular physical exercise, a nutritious diet, and sufficient sleep, help regulate dopamine levels. Managing stress and practicing mindfulness techniques can also contribute to balanced dopamine levels. By nurturing overall well-being, individuals can create positive social environments and experiences.
Key Influences on Dopamine in Social Interactions
- Positive social feedback
- Physical touch and affection
- Empathy and emotional connection
- Successful communication and validation
- Group cooperation and shared activities
- Romantic involvement
- Social media interactions
Watch Live Sports Now!
Dont miss a single moment of your favorite sports. Tune in to live matches, exclusive coverage, and expert analysis.
Start watching top-tier sports action now!
Watch NowTips for Boosting Dopamine Naturally
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Practice mindfulness and meditation to reduce stress.
- Spend quality time with loved ones.
- Pursue creative activities that bring you joy.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Seek out social recognition and praise.
- Limit excessive social media use to avoid overstimulation.
Pro Tip: Engaging in meaningful, face-to-face interactions rather than relying solely on social media can lead to a more fulfilling dopamine response and stronger, more genuine connections.
| Aspect | Positive Social Interaction | Negative Social Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine Release | Increased release, fostering connection | Reduced release, causing disengagement |
| Emotional Impact | Happiness, satisfaction, bonding | Anxiety, discomfort, isolation |
| Social Motivation | Encourages ongoing engagement | Promotes withdrawal and avoidance |
“The key to meaningful social interactions is understanding how dopamine shapes our connections, helping us form bonds that last a lifetime.”
Social interactions are fundamental to human well-being, and dopamine is the chemical that powers these connections. By understanding how dopamine influences our social behavior, we can foster healthier, more positive relationships. Whether it’s bonding with family, connecting with friends, or engaging in romantic partnerships, dopamine plays a pivotal role in shaping these experiences. Share this post with your social network, bookmark it for later, and take steps to ensure you nurture the positive social interactions in your life. By managing dopamine levels and cultivating meaningful connections, you can lead a more fulfilling social life.