Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms and affect almost any part of the body. The exact cause of autoimmune diseases remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. Understanding autoimmune disease is crucial because it helps in the early identification and effective management of these conditions. In this article, we’ll explore what autoimmune diseases are, how they develop, common symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments for people living with these disorders.
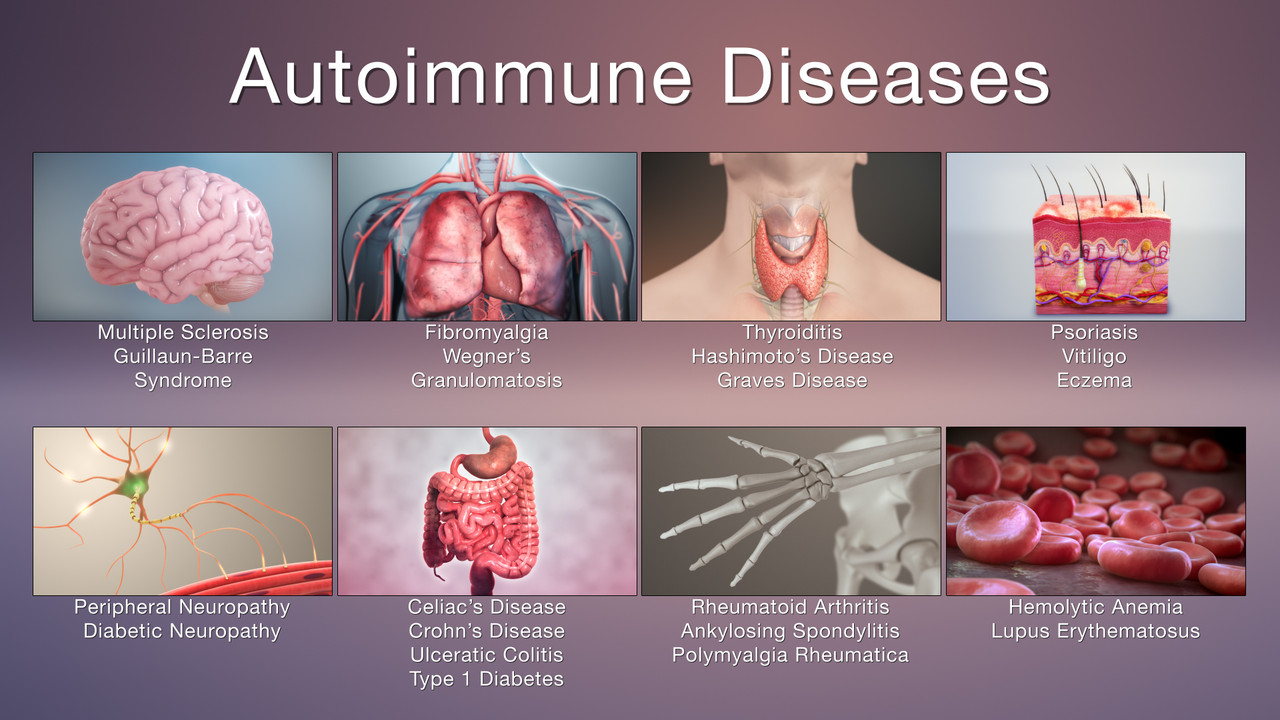
What is an Autoimmune Disease?
An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system, which is supposed to protect the body from harmful invaders, starts attacking its own cells. The immune system’s primary function is to fight off viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens, but in autoimmune conditions, it becomes misdirected. These diseases can range from mild to severe, depending on the organ or tissue being attacked. Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis. Understanding autoimmune disease requires recognizing that the immune system is malfunctioning, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary greatly depending on the specific condition and the part of the body affected. However, general symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and digestive issues. Many autoimmune diseases cause widespread inflammation, which can lead to pain and swelling in different parts of the body. Flare-ups of symptoms are common, where the condition worsens for a period of time before improving. If left untreated, these diseases can lead to permanent damage to organs or systems within the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the precise cause of autoimmune diseases is unknown, several factors contribute to their development. Genetic factors play a significant role, as autoimmune diseases often run in families. Environmental triggers such as infections, stress, and exposure to certain chemicals may also increase the risk of developing an autoimmune disease. Hormonal imbalances are another factor, which is why autoimmune diseases are more common in women than men. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventative measures and seek earlier treatment.
Diagnosis of Autoimmune Diseases
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be complex because their symptoms often mimic those of other health conditions. Blood tests are commonly used to detect specific antibodies that may indicate an autoimmune disorder. Doctors may also conduct imaging tests and biopsies to assess the damage done by the immune system. Because there is no single test to diagnose autoimmune diseases, physicians often use a combination of methods to identify the condition. Early diagnosis is key to managing symptoms and preventing long-term damage to organs.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Diseases
Treatment for autoimmune diseases typically focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Immunosuppressive medications are commonly prescribed to suppress the overactive immune response. These drugs can reduce inflammation and prevent the immune system from attacking healthy cells. Depending on the disease, doctors may also recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling. Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system, offering relief for certain conditions.
Vote
Who is your all-time favorite president?
Lifestyle Adjustments for Autoimmune Disease Management
Managing autoimmune diseases often requires changes in lifestyle to improve quality of life and reduce symptoms. Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques such as yoga and meditation can also contribute to overall well-being. Avoiding triggers like smoking or exposure to environmental toxins can help reduce flare-ups and prevent disease progression. Working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan is crucial to managing the condition effectively.
The Role of Diet in Autoimmune Disease
While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for autoimmune disease sufferers, some foods are known to exacerbate inflammation. Anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, nuts, and berries may help reduce inflammation and support the immune system. Avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and high-fat diets is also recommended for those with autoimmune disorders. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids through foods like salmon or chia seeds can help balance the immune system and reduce inflammation. A healthy gut is also essential for people with autoimmune conditions, so including fiber-rich foods can be beneficial.
Mental Health and Autoimmune Disease
Living with an autoimmune disease can take a toll on mental health, as chronic illness often leads to stress, anxiety, and depression. Psychological support is vital for individuals with autoimmune diseases to help them cope with the emotional burden of their condition. Talking to a counselor or joining a support group can help individuals manage their mental health while dealing with physical symptoms. Mind-body techniques, such as mindfulness and breathing exercises, have also been shown to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Taking care of both the body and mind is essential for managing autoimmune diseases.
The Impact of Autoimmune Disease on Daily Life
For many individuals, autoimmune diseases can have a significant impact on daily life. These conditions can interfere with work, family life, and social activities due to chronic pain, fatigue, and unpredictable flare-ups. Time management becomes crucial as individuals with autoimmune diseases may need to rest more often or adjust their schedules to accommodate treatment regimens. Support from family and friends can also play a critical role in helping individuals manage the challenges of living with an autoimmune disease. Adapting to life with an autoimmune disease requires patience, perseverance, and a proactive approach to self-care.
Autoimmune Diseases and Prevention
While autoimmune diseases are not always preventable, there are ways to reduce the risk of developing one. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can lower the likelihood of an autoimmune disease developing. Additionally, early detection and treatment of any underlying conditions, such as infections or hormonal imbalances, can prevent autoimmune disorders from emerging. Genetic testing may also offer insights for individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases. Staying informed and vigilant can help individuals minimize their risk and manage any health issues before they become more serious.
Key Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Painful or swollen joints
- Skin rashes or lesions
- Digestive issues such as bloating or diarrhea
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Numbness or tingling in the limbs
- Persistent fever or inflammation
Watch Live Sports Now!
Dont miss a single moment of your favorite sports. Tune in to live matches, exclusive coverage, and expert analysis.
Start watching top-tier sports action now!
Watch NowTips for Managing Autoimmune Diseases
- Follow your prescribed treatment plan
- Eat an anti-inflammatory diet
- Get enough sleep each night
- Practice stress management techniques
- Stay active with regular exercise
- Avoid environmental triggers such as chemicals and pollutants
- Stay hydrated and maintain overall wellness
Pro Tip: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help manage autoimmune disease progression and make adjustments to treatment as needed.
| Preventive Measure | Benefit | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | Reduces inflammation and supports immune function | Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods into your daily diet |
| Stress Management | Reduces flare-ups and improves overall well-being | Practice yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises |
| Regular Exercise | Boosts energy and strengthens the immune system | Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise daily |
“Managing an autoimmune disease requires a balanced approach, combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes and emotional support.”
Living with an autoimmune disease may present challenges, but it is possible to lead a fulfilling life with the right approach. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can take control of their health and improve their quality of life. Don’t hesitate to share this information with others who may be affected by autoimmune diseases. Bookmark this article as a helpful guide, and share it on social media to raise awareness about autoimmune conditions. Together, we can help those living with autoimmune diseases lead healthier, happier lives.